AI Agent Observability Best Practices for Reliable and Compliant Systems
Introduction
As autonomous AI systems make decisions impacting customers, operations, and compliance, the question “What is our AI doing, and why?” becomes critical. AI agent observability separates production-ready systems from experimental prototypes, enabling organizations to monitor, understand, and govern autonomous behaviors in real-time. Without comprehensive AI monitoring and governance, even sophisticated agents become operational risks.
This guide explores best practices for implementing observability in autonomous AI, building governed AI systems, and ensuring reliable AI agents that deliver value while maintaining compliance, trust, and accountability.
What Is AI Agent Observability?
AI agent observability extends beyond traditional monitoring, providing visibility into autonomous decision-making processes, reasoning chains, tool usage, and outcome patterns. While conventional systems track metrics like latency and error rates, agentic AI requires understanding why decisions were made, how agents reasoned through problems, and what actions were taken autonomously.
Core Components:
- Decision Tracing: Complete audit trails of reasoning steps and choices
- Action Logging: Records of all autonomous actions across systems
- Performance Metrics: Success rates, accuracy, efficiency measurements
- Behavior Analysis: Pattern detection in agent decision-making
- Anomaly Detection: Identifying unexpected or problematic behaviors
Unlike black-box AI, observable agents provide transparency essential for debugging, compliance, optimization, and stakeholder trust.
Why Observability Matters for Agentic AI
Autonomous agents operate with minimal human oversight, making observability non-negotiable:
- Compliance Requirements: Regulators demand explainability for automated decisions affecting customers, financial services, healthcare, and hiring. Ethical AI deployment requires demonstrating fair, non-discriminatory decision-making through comprehensive logging and analysis.
- Operational Reliability: AI system reliability depends on quickly identifying when agents deviate from expected behaviors, make suboptimal decisions, or encounter edge cases requiring intervention.
- Performance Optimization: Without visibility into agent reasoning and outcomes, improving performance becomes guesswork. AI agent performance monitoring reveals bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and optimization opportunities.
- Risk Management: Autonomous systems can propagate errors at scale. Early detection through observability prevents minor issues from becoming major incidents affecting thousands of customers or transactions.
- Stakeholder Trust: Customers and employees need assurance that AI agents operate responsibly. Transparency through observability builds confidence in autonomous systems.
Best Practices for Reliable and Compliant Systems
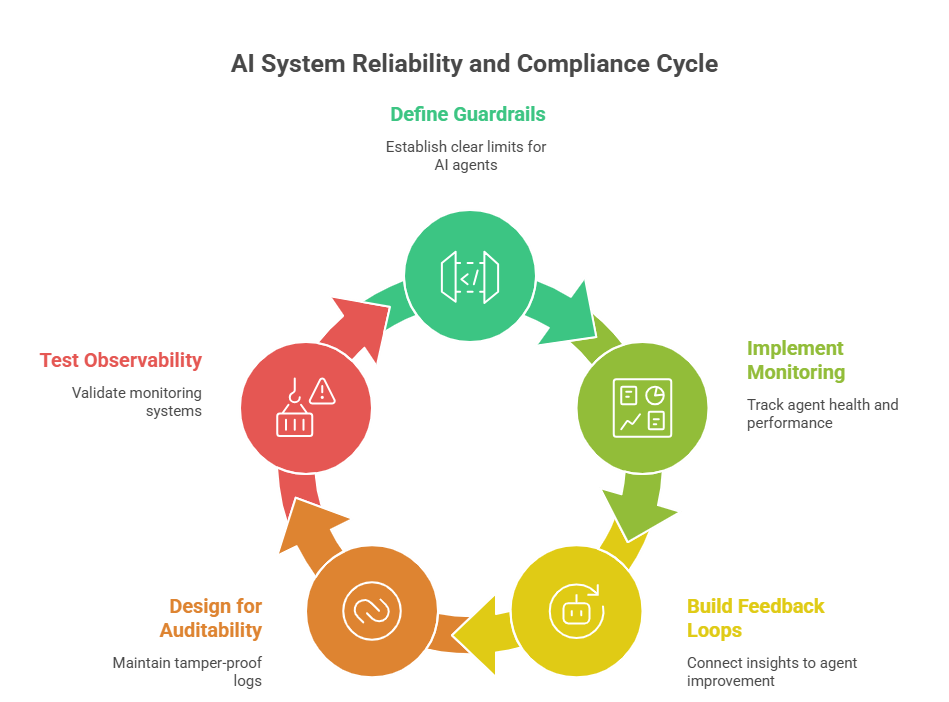
As AI becomes central to business operations, ensuring systems are reliable and compliant is essential. Clear monitoring, feedback, and governance help AI agents operate safely and improve over time.
1. Define Operational Guardrails and Boundaries
Establish clear limits for AI agents, specifying what they can do and when human oversight is required. This prevents unintended actions and ensures compliance with business rules.
Use pre-execution validation and post-action verification to catch errors early. Approval thresholds and automated rollback mechanisms help maintain safety and accountability in high-risk scenarios.
2. Implement Progressive Monitoring
Start with detailed logging during development to identify issues, then optimize as patterns emerge. This approach balances visibility, performance, and cost.
Real-time dashboards track agent health, errors, and resource usage. Focusing on critical decision paths over time ensures efficient monitoring and timely detection of anomalies.
3. Build Feedback Loops
Building feedback loops connects observability insights to agent improvement through retraining, prompt optimization, and workflow refinement. This enables continuous learning and better performance.
Regularly analyzing data and incorporating user feedback allows iterative updates to policies and agent behavior. These feedback loops ensure AI agents remain aligned with evolving business objectives and operational requirements.
4. Design for Auditability
Maintain tamper-proof logs and cryptographic verification to support compliance and investigation. Immutable records help track decisions and actions reliably.
Implement efficient search, retrieval, and privacy controls for sensitive information. Clear audit trails ensure readiness for regulatory reviews and operational oversight.
5. Test Observability Before Deployment
Validate monitoring systems under production conditions, ensuring dashboards, alerts, and logs provide actionable insights.
Perform load testing, alert checks, and query evaluations. This confirms the observability framework works effectively before AI agents go live.
Also Read : AI Browser Agents: Automating Web-Based Tasks with Intelligent Systems
Conclusion
AI agent observability transforms autonomous AI from experimental technology into production-grade systems delivering reliable, compliant, and optimized performance. Implementing comprehensive AI monitoring and governance enables governed AI systems that stakeholders trust and regulators approve.
Building reliable AI agents requires observability, governance, and continuous monitoring. Amplework, a top AI agent development company, ensures scalable, compliant, and trustworthy AI solutions. Amplework’s expertise helps organizations reduce risks and confidently deploy autonomous AI systems.


 sales@amplework.com
sales@amplework.com
 (+91) 9636-962-228
(+91) 9636-962-228