Reasoning in Agentic AI: How Modern LLM Agents Make Decisions
Introduction
Traditional AI systems follow predetermined rules and respond to specific inputs predictably. They can’t adapt to novel situations, break down complex problems, or make multi-step decisions autonomously. This limitation restricts AI to narrow, well-defined tasks requiring constant human oversight and intervention for anything beyond basic functionality.
Agentic AI reasoning represents a fundamental shift, systems that think through problems, plan approaches, and make autonomous decisions across multiple steps. Modern LLM agents don’t just respond to prompts; they analyze situations, consider options, plan actions, and adapt based on outcomes. Understanding how reasoning in LLM agents works reveals why these systems are transforming what AI can accomplish independently.
What Is Agentic AI Reasoning?
Agentic AI reasoning refers to the ability of AI systems to break down complex goals into steps, evaluate options, make decisions, take actions, and adjust approaches based on results. Unlike simple prompt-response systems, agentic AI engages in deliberate problem-solving involving planning, execution, observation, and adaptation. This autonomous AI decision system capability enables handling complex, multi-step tasks without constant human guidance.
The Agentic Loop Reasoning Step Process
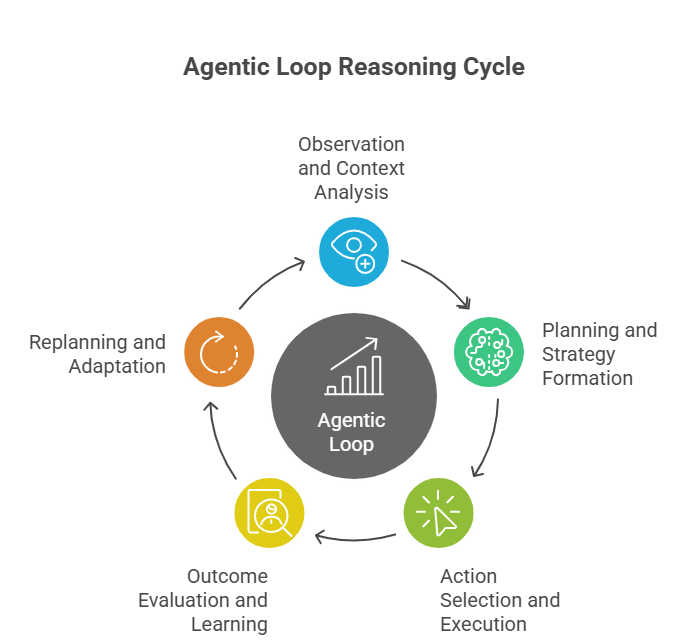
1. Observation and Context Analysis
The agentic loop reasoning step begins with observation. AI agents assess their situation, available information, and environmental context.
Observation activities include:
- Input data analysis
- Context retrieval from memory
- State assessment and evaluation
- Goal relevance determination
Strong observation ensures agents make decisions based on a complete, accurate situational understanding.
2. Planning and Strategy Formation
After observation, agents develop approaches to achieve goals by breaking objectives into manageable subtasks, sequencing actions logically, and considering alternatives.
Planning components include:
- Goal decomposition into steps
- Action sequence determination
- Resource requirement assessment
- Alternative strategy consideration
Sophisticated planning enables agents to tackle complex challenges beyond simple reactive systems.
3. Action Selection and Execution
With plans established, agents select actions, weighing outcomes, costs, success probability, and goal alignment, then execute actions through tools, API calls, or environment interactions.
Action execution involves:
- Option evaluation and comparison
- Decision criteria application
- Execution timing optimization
- Tool and resource utilization
Effective selection balances exploration of new approaches with exploitation of known successful strategies.
4. Outcome Evaluation and Learning
After executing actions, agents evaluate results, comparing expected versus actual outcomes and extracting lessons for future decisions.
Evaluation activities include:
- Result comparison to expectations
- Success metric assessment
- Pattern recognition across attempts
- Learning integration into knowledge
Continuous evaluation enables agents to improve decision quality through experience.
5. Replanning and Adaptation
Based on the evaluation, agents adjust approaches. If results fall short, they replan, trying alternatives or seeking additional information before proceeding.
Adaptation mechanisms include:
- Strategy adjustment based on feedback
- Alternative approach exploration
- Resource reallocation decisions
- Goal refinement when necessary
Adaptive replanning allows agents to succeed despite incomplete information or changing circumstances.
Chain-of-Thought in AI Agents
Chain-of-thought reasoning makes an agent’s decision processes transparent and verifiable. Rather than jumping directly to answers, agents explicitly articulate reasoning steps, observations, considerations, logic, and conclusions. This transparency enables debugging, trust building, and quality assurance for autonomous systems.
Chain-of-thought benefits include:
- Explainable decision processes
- Error identification and debugging
- Reasoning quality assessment
- Human oversight enablement
- Trust and confidence building
Transparent reasoning proves critical for deploying autonomous AI in high-stakes business environments.
Challenges in Agentic AI Reasoning
- Reasoning Quality and Reliability: Agent reasoning may produce errors due to flawed assumptions or incomplete data. Validation, human oversight, and error detection improve reliability.
- Computational Cost: Deep reasoning needs multiple LLM calls, increasing latency and costs. Optimizing depth, caching, and tiered reasoning reduces overhead.
- Context Window Limitations: Long reasoning chains can exceed model context limits. Memory systems, summarization, and selective retention maintain continuity.
- Evaluation and Debugging: Examining reasoning chains is needed to understand agent decisions. Visualization, auditing, and performance analysis enhance trust and improvement.
Also Read : Understanding Large Language Models (LLMs)
The Amplework Agentic AI Development Advantage
At Amplework Software, we specialize in building sophisticated agentic AI systems with robust reasoning capabilities. Our LLM agent development expertise encompasses planning systems, decision-making frameworks, and adaptive execution engines that enable truly autonomous AI agents.
Our Agentic AI Development Services Include:
- Custom reasoning architecture design
- Multi-step planning system implementation
- Chain-of-thought integration
- Tool usage and action execution frameworks
- Monitoring and evaluation systems
Our AI services extend beyond basic LLM integration to sophisticated agentic systems capable of autonomous decision-making and complex task execution. We build agents that don’t just respond but truly reason through challenges.
Final Words
Agentic AI reasoning represents the evolution from reactive AI systems to autonomous agents capable of genuine problem-solving and decision-making. These systems don’t just follow instructions; they think through challenges, plan approaches, and adapt strategies based on outcomes.
Understanding reasoning mechanisms in agentic AI reveals both the tremendous potential and current limitations. Organizations implementing agentic systems gain capabilities for automating complex workflows, solving sophisticated problems, making autonomous decisions at scale, and leveraging generative AI services to enhance creativity and efficiency.


 sales@amplework.com
sales@amplework.com
 (+91) 9636-962-228
(+91) 9636-962-228