AI Translation Proof of Concept: Step-by-Step Setup Guide
Introduction
Many businesses need translation capabilities but hesitate to invest in full systems without validation. They wonder if AI translation will handle their specific content, terminology, and quality requirements. Jumping directly to production implementation risks expensive failures if AI doesn’t meet actual needs or work with domain-specific language.
An AI translation proof of concept validates feasibility quickly with minimal investment before committing to full deployment. A well-designed translation AI demo tests accuracy with real content, evaluates different approaches, and provides confidence for informed decisions. This step-by-step guide walks through setting up effective AI translation POCs that deliver actionable insights.
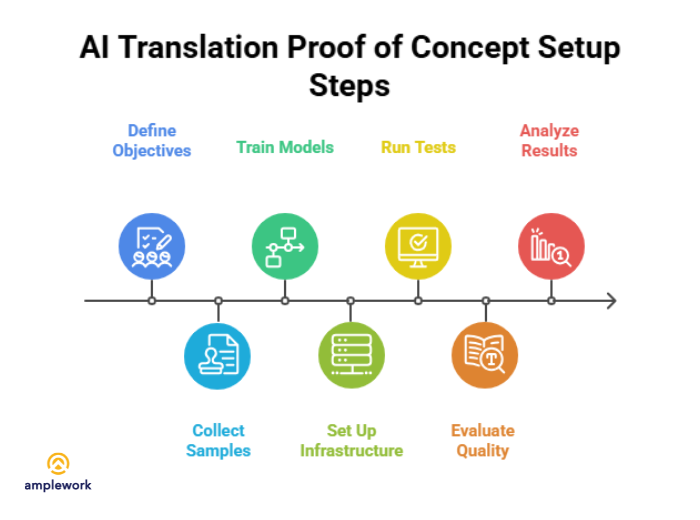
Step 1: Define Clear POC Objectives
Start by establishing specific goals for your AI translation proof of concept. Don’t aim for general “testing translation”; define precise success criteria, target languages, content types, and quality thresholds. Clear objectives guide technology selection and enable objective evaluation.
Key objectives to define:
- Target language pairs needed
- Content types and domains
- Minimum acceptable accuracy levels
- Speed and volume requirements
- Budget and timeline constraints
Document these objectives as measurable criteria determining POC success or failure.
Step 2: Collect Representative Content Samples
Gather real content samples representing actual translation needs. Include diverse examples, simple and complex sentences, technical terminology, industry jargon, and edge cases. Representative samples ensure POC results reflect production reality rather than idealized scenarios.
Content collection includes:
- 100-500 sentences per language pair
- Mix of content complexity levels
- Domain-specific terminology examples
- Edge cases and challenges
- Existing human translations for comparison
Quality sample selection determines POC relevance and reliability.
Step 3: Train or Fine-Tune Translation Models
Beyond testing pre-trained systems, consider AI model training on your domain-specific content to improve handling of terminology, style, and context. Even limited training on representative samples can reveal gains over generic models.
Key actions for this step:
- Select base models suitable for your languages and domains
- Fine-tune on collected content samples, including edge cases
- Experiment with limited epochs to avoid overfitting
- Evaluate intermediate results to refine the training dataset
- Compare fine-tuned model outputs with pre-trained alternatives
This ensures your AI translation POC tests not just off-the-shelf solutions but also customized approaches for your content and quality needs.
Step 4: Set Up Translation Testing Infrastructure
Create a simple infrastructure for running translations and collecting results. This doesn’t require production-grade systems; basic scripts calling APIs or running models locally suffice for POC purposes. Focus on collecting data for evaluation rather than building a scalable architecture.
Infrastructure components:
- API integration scripts
- Batch processing capabilities
- Result storage and organization
- Error handling and logging
- Cost tracking mechanisms
Keep infrastructure lean, focusing on evaluation rather than production readiness.
Step 5: Run Translation Tests
Execute translations across all sample content using each approach being evaluated. Process samples through different systems systematically, documenting results, processing times, and any errors. Consistent testing methodology enables fair comparison across approaches.
The testing process includes:
- Systematic sample processing
- Consistent parameter usage
- Processing time measurement
- Error and failure logging
- Cost per translation tracking
Thorough testing reveals performance patterns across content types and complexity levels.
Step 6: Evaluate Translation Quality
Quality evaluation combines automated metrics and human review. Automated metrics (BLEU, TER) provide a quick assessment but miss nuances. Human evaluation by bilingual reviewers or professional translators validates actual quality and usability for your specific needs.
Evaluation methods include:
- Automated metric calculation
- Side-by-side human comparison
- Domain expert review
- Error categorization and analysis
- Acceptability rating collection
Balance automated efficiency with human judgment for comprehensive quality assessment.
Step 7: Analyze Results and Make Recommendations
Compile findings comparing approaches across quality, speed, cost, and ease of implementation. Identify which approaches meet the success criteria and which fall short. Provide clear recommendations for next steps, full implementation, additional testing, or alternative solutions.
Analysis deliverables include:
- Quality comparison charts
- Cost-benefit analysis
- Speed and scalability assessment
- Implementation complexity evaluation
- Go/no-go recommendations
Actionable recommendations based on objective data enable confident decisions about production deployment.
Best Practices for Translation AI Demo Success
- Use Real Content: Synthetic or simplified samples produce misleading results. Test with actual content requiring translation.
- Include Edge Cases: Test challenging content, revealing approach limitations and failure modes.
- Involve End Users: Have actual translators or content consumers evaluate quality from their perspective.
- Document Everything: Record decisions, findings, and lessons learned for future reference and knowledge transfer.
- Plan for Iteration: First AI POC attempts are rarely perfect. Budget time for adjustments and additional testing.
- Consider Maintenance: Evaluate ongoing costs for model updates, API changes, and quality maintenance beyond initial setup.
Common AI Translation POC Challenges
Handling Context and Ambiguity
Short text segments lose context, affecting translation quality. Evaluate whether approaches need larger context windows or document-level translation capabilities.
Cost at Scale
POC costs differ dramatically from production volumes. Project costs are accurately based on expected translation volumes, avoiding surprise expenses at scale.
Integration Complexity
Some translation approaches integrate easily, while others require significant engineering. Assess integration effort realistically as part of the total cost of ownership.
Also Read : AI Proof of Concept Use Cases: Practical Business Examples Across Industries
Final Words
An AI translation proof of concept validates feasibility and quality before major implementation investments. Following structured POC processes with clear objectives, representative content, and thorough evaluation produces actionable insights guiding confident decisions.
Amplework Software delivers AI translation proof of concept projects with clear outcomes, covering design, testing, evaluation, and roadmaps, leveraging NLP development expertise across legal, technical, and marketing content.


 sales@amplework.com
sales@amplework.com
 (+91) 9636-962-228
(+91) 9636-962-228