Agentic AI Security: Defending the Next Era of Autonomous Technology
Introduction
As LLM-powered autonomous agents evolve from experimental prototypes to production systems making real business decisions, agentic AI security has emerged as a critical concern for enterprises. Unlike traditional AI that passively analyzes data, autonomous agents take actions, access systems, execute workflows, and interact with customers, creating unprecedented security implications when compromised.
Understanding agentic AI security risks, implementing robust agentic AI data protection, and deploying comprehensive agentic AI security solutions aren’t optional considerations; they’re business imperatives.
This guide covers AI agent security risks and offers practical strategies to secure autonomous AI without limiting operational flexibility.
Understanding Agentic AI and Its Security Implications
LLM-powered autonomous agents represent AI’s next evolution, systems that plan multi-step workflows, use tools, access databases, interact with APIs, and make decisions without constant human oversight. While traditional AI models simply predict or generate outputs, agentic AI takes autonomous action based on those predictions.
The Security Difference: Traditional AI security focuses on model integrity, data privacy, and prediction accuracy. Agentic AI security must additionally address autonomous action validation, tool access control, multi-system orchestration, and preventing unintended consequences from AI decisions propagating across enterprise systems.
Critical Agentic AI Security Risks
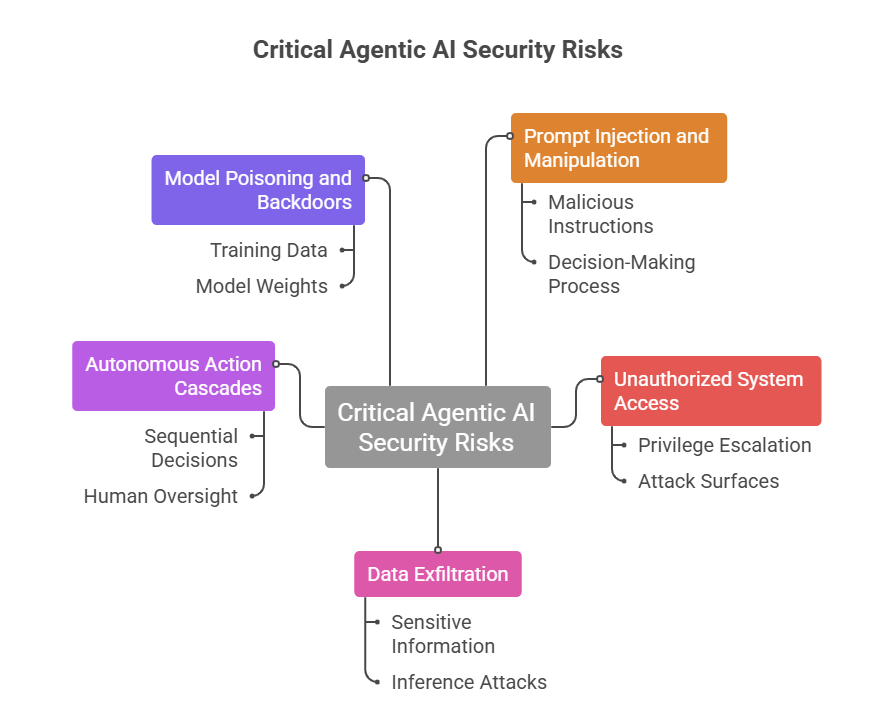
Understanding AI agent security risks enables proactive defense rather than reactive damage control:
1. Prompt Injection and Manipulation
Risk: Attackers manipulate agent prompts, injecting malicious instructions that override intended behavior. Unlike traditional injection attacks targeting databases, prompt injection targets the agent’s decision-making process.
Example: A customer service agent designed to help users could be tricked into revealing sensitive information, executing unauthorized actions, or providing false information through carefully crafted prompts embedded in user messages.
Impact: Unauthorized data access, system manipulation, reputational damage, and compliance violations.
2. Unauthorized System Access
Risk: Compromised agents accessing systems beyond their intended scope. Autonomous agents require broad permissions to function effectively, creating attack surfaces when those permissions are exploited.
Example: An agent designed to query sales databases gains access to financial systems through privilege escalation, potentially exfiltrating sensitive data or executing unauthorized transactions.
Impact: Data breaches, financial fraud, regulatory penalties, and operational disruption.
3. Data Exfiltration Through Agent Interactions
Risk: Agentic AI data protection becomes complex when agents process sensitive information across multiple systems. Attackers may extract confidential data through seemingly innocuous agent interactions.
Example: An agent summarizing customer records inadvertently includes personally identifiable information in outputs logged to insecure systems or revealed through inference attacks.
Impact: Privacy violations, GDPR/CCPA penalties, customer trust erosion, and competitive intelligence loss.
4. Autonomous Action Cascades
Risk: Agents making sequential decisions without human oversight can propagate errors or malicious actions across systems before detection.
Example: A compromised trading agent executes unauthorized transactions across multiple accounts. By the time anomalies are detected, significant financial damage has occurred.
Impact: Financial losses, operational disruptions, and potential system-wide failures.
5. Model Poisoning and Backdoors
Risk: Training data or model weights compromised during development, creating backdoors that activate under specific conditions.
Example: An agent trained on poisoned data behaves normally under standard conditions but executes malicious actions when triggered by specific inputs invisible during testing.
Impact: Long-term security compromises are difficult to detect and remediate.
Agentic AI Security Solutions
Comprehensive agentic AI security solutions combine multiple defensive layers:
- Input Validation and Sanitization: Filter and validate all inputs before processing, detecting, and blocking prompt injection attempts.
- Output Filtering: Monitor agent outputs, preventing sensitive data leakage, ensuring responses align with security policies.
- Behavioral Analytics: Deploy ML-based anomaly detection, identifying unusual agent behavior patterns indicating compromise or malfunction.
- Automated Rollback: Implement mechanisms that automatically reverse agent actions when security violations are detected.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct penetration testing specifically targeting agent vulnerabilities, including prompt injection, privilege escalation, and data exfiltration.
How to Secure Agentic AI: Implementation Roadmap
- Foundation (Weeks 1-4): Assess current agent security posture, identify critical risks, and establish baseline security controls.
- Core Controls (Weeks 5-12): Implement access controls, monitoring infrastructure, and human-in-the-loop safeguards.
- Advanced Protection (Weeks 13-20): Deploy behavioral analytics, automated response systems, and comprehensive audit capabilities.
- Continuous Improvement (Ongoing): Regular security assessments, threat modeling updates, and control refinement based on emerging threats.
Also Read : Scalability Issues in Agentic AI: Best Practices for Digital Transformation Architects
Why Choose Amplework
Amplework provides end-to-end custom AI solutions tailored to enterprise needs. With expertise in risk assessment, secure deployment, and continuous monitoring, Amplework helps organizations protect autonomous AI agents, mitigate emerging threats, and confidently leverage AI’s full potential without compromising performance or scalability.
Conclusion
Agentic AI can transform enterprises but brings unique security risks, including prompt injection, unauthorized access, and model poisoning. Implementing layered safeguards, input validation, output monitoring, behavioral analytics, and audits allows organizations to use autonomous AI safely, protecting data, operations, and trust while maintaining flexibility and business-critical workflows.


 sales@amplework.com
sales@amplework.com
 (+91) 9636-962-228
(+91) 9636-962-228