What Happens During the Perception Step in the Agentic AI Loop?
Introduction
Most people think AI agents simply respond to prompts and execute commands. They miss the critical first step that determines whether agents succeed or fail: perception. Without properly understanding their environment, available information, and current context, AI agents make poor decisions regardless of how sophisticated their reasoning capabilities might be.
Agentic AI perception forms the foundation of the entire AI reasoning loop. During this crucial step, agents gather information, interpret their environment, retrieve relevant context, and assess their current state relative to goals. Understanding the perception step in the agentic AI loop reveals why some agents perform brilliantly while others with similar models struggle with basic tasks.
What Is Agentic AI Perception?
Agentic AI perception encompasses all activities where agents sense, interpret, and understand their operational environment before taking action. This includes processing inputs, retrieving relevant memories, assessing available tools, understanding constraints, and evaluating the current state against desired goals. Perception transforms raw data into a meaningful understanding that informs subsequent reasoning and decision-making.
The Perception Step in the Agentic AI Workflow
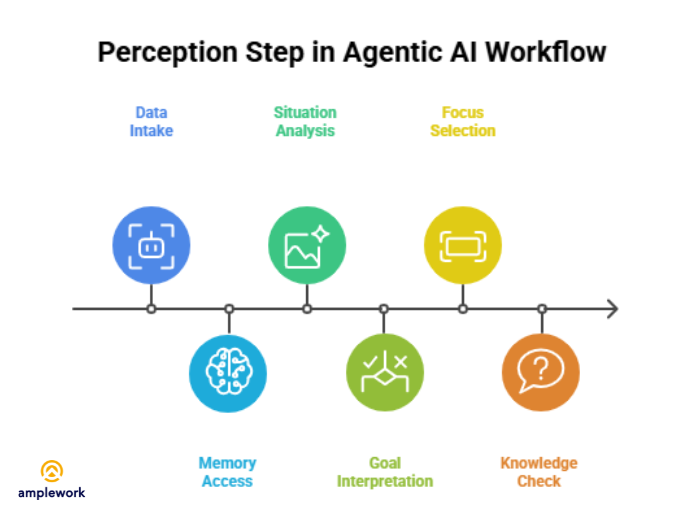
1. Input Reception and Initial Processing
The perception step begins when agents receive inputs, user requests, system events, sensor data, or triggered conditions. In LLM agent development, perception starts by parsing these inputs, identifying their type and format, and extracting key information. This initial processing converts raw inputs into structured information that the agent can work with.
Input processing includes:
- Data format identification and parsing
- Key information extraction
- Input type classification
- Priority level determination
- Urgency assessment
Strong input processing ensures agents don’t misinterpret requests or miss critical information buried in complex inputs.
2. Context and Memory Retrieval
After processing inputs, agents retrieve relevant context from various memory systems. This includes conversation history, previous interactions, stored knowledge, and learned patterns. AI perception models access short-term working memory, long-term knowledge bases, and episodic memory of past actions and outcomes.
Memory retrieval involves:
- Conversation history review
- Related past interaction identification
- Relevant knowledge base searching
- Similar case pattern matching
- Learned preference application
Effective context retrieval ensures agents make decisions informed by relevant history rather than treating each interaction as isolated.
3. Environmental State Assessment
Agents assess their current operational environment, what systems are available, what data they can access, what tools they can use, and what constraints they face. This environmental awareness prevents agents from attempting impossible actions or making plans requiring unavailable resources.
State assessment includes:
- Available tool inventory
- System status checking
- Resource availability verification
- Permission and access validation
- Constraint identification
Understanding the environmental state prevents wasted effort on unexecutable plans and enables realistic decision-making.
4. Goal Understanding and Decomposition
Agents interpret what they’re actually being asked to accomplish. Complex requests require decomposition into specific, achievable goals. This goal understanding involves identifying explicit requests, inferring implicit intentions, and recognizing success criteria.
Goal analysis includes:
- Primary objective identification
- Implicit requirement inference
- Success criteria definition
- Constraint recognition
- Priority determination
Misunderstanding goals leads to perfectly executed but ultimately useless actions. Strong goal perception ensures agents work toward correct objectives.
Also Read : How to Build Feedback Loops in Agentic AI for Continuous Digital Transformation
5. Relevance Filtering and Prioritization
Not all perceived information is equally important. Agents filter massive amounts of available data, identifying what’s most relevant to current goals. This prioritization focuses attention and computational resources on information that actually matters for decision-making.
Filtering activities include:
- Information relevance scoring
- Priority ranking application
- Noise elimination
- Critical detail highlighting
- Context window optimization
Effective filtering prevents information overload while ensuring critical details receive appropriate attention.
6. Uncertainty and Gap Identification
During perception, agents identify what they don’t know, information gaps, ambiguities, and uncertainties. Recognizing these gaps enables agents to seek clarification, make reasonable assumptions, or flag issues requiring human input before proceeding.
Gap identification includes:
- Missing information detection
- Ambiguity recognition
- Assumption requirement identification
- Confidence level assessment
- Clarification need determination
Acknowledging uncertainty prevents agents from confidently pursuing actions based on incomplete or misunderstood information.
How Agentic AI Works: From Perception to Action
Perception feeds directly into subsequent agentic AI workflow stages. Quality perception enables quality reasoning; agents with accurate environmental understanding make better plans and decisions. Poor perception cascades through the entire loop, causing errors in reasoning, planning, and execution.
The perception-to-action flow:
- Perception: Understand the current situation
- Reasoning: Analyze options and implications
- Planning: Develop action sequences
- Execution: Carry out planned actions
- Observation: Perceive results, and the cycle continues
This AI reasoning loop depends critically on perception quality at each iteration.
Related Blog : Agentic AI Loops Explained: Perception, Reasoning, Action & Feedback
Improving Perception in AI Agents
- Structured Memory Systems: Implement hierarchical memory architectures organizing information by relevance, recency, and importance for efficient retrieval.
- Semantic Search: Use vector embeddings and semantic similarity for finding relevant context even when exact keywords don’t match.
- Active Learning: Build feedback loops where agents learn which information proves most valuable for different task types.
- Multimodal Integration: Develop unified perception frameworks processing diverse input types into a coherent understanding.
- Confidence Scoring: Implement mechanisms where agents assess their perception confidence, triggering clarification when uncertain.
Conclusion
Agentic AI perception is crucial for success. Strong perception enables accurate reasoning, effective planning, and reliable execution, while weak perception causes cascading failures despite sophisticated downstream components.At Amplework, our AI development services design agents with robust perception systems and thoughtful architecture. Our expertise ensures agents understand situations fully, integrating multi-source data, context retrieval, and intelligent prioritization before taking action.


 sales@amplework.com
sales@amplework.com
 (+91) 9636-962-228
(+91) 9636-962-228