AI Data Modelling: How Data Is Structured Before Model Training
Introduction
Many AI projects fail not because of weak algorithms but due to poor data preparation. Teams often train models on raw, unstructured data, causing weak performance, longer training time, and failed deployments.
AI data modelling sets the foundation by structuring data before training. Strong data modelling turns raw information into high-quality, training-ready datasets. In this blog, we discuss how AI data modelling structures raw data before training. You’ll learn key steps and why proper preparation improves model performance.
What Is AI Data Modelling?
AI data modelling involves organizing and structuring raw data so machine learning algorithms can interpret it effectively. It includes designing schemas, defining relationships, selecting data types, and standardizing formats to ensure smooth processing.
It also focuses on feature engineering, feature selection, and optimizing data for algorithm needs. Proper modelling improves learning accuracy, efficiency, and overall model performance.
The Data Structuring Process
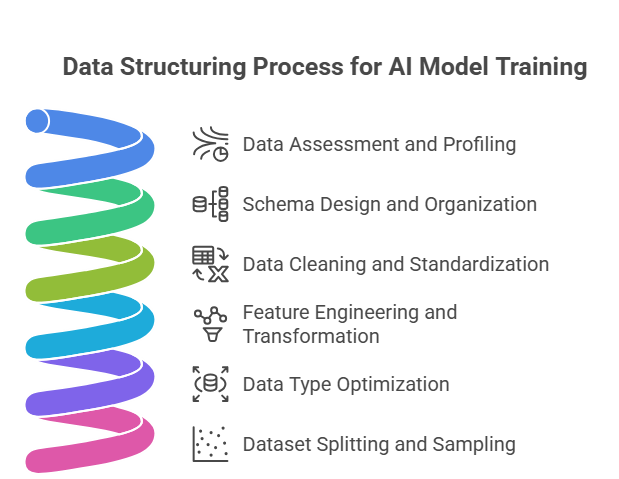
1. Data Assessment and Profiling
Data assessment helps teams understand data sources, quality, distributions, missing values, and anomalies before structuring begins. Profiling reveals important patterns and potential issues that influence modelling decisions. Proper assessment prevents accidental loss of valuable information and reduces the risk of biases that can affect model performance during training.
2. Schema Design and Organization
Schema design defines how data is structured, connected, and stored. It organizes tables, relationships, and data types to ensure consistency and efficient retrieval. A strong schema keeps data clean and accessible. For large datasets, good schema organization improves training speed, reduces computational load, and supports scalable AI workflows.
3. Data Cleaning and Standardization
Data cleaning removes duplicates, fixes errors, handles missing values, and resolves inconsistencies. Standardization aligns formats, units, and naming conventions to create uniform inputs. Clean, standardized data reduces noise, prevents unpredictable model behavior, and ensures algorithms learn from reliable, high-quality information during AI model training across different scenarios.
4. Feature Engineering and Transformation
Feature engineering transforms raw data into meaningful inputs that highlight useful patterns. It includes creating new variables, summarizing information, extracting time-based features, and encoding text or categories. Effective feature engineering improves model accuracy while reducing complexity, allowing algorithms to learn relationships more efficiently and with less computational effort.
5. Data Type Optimization
Data type optimization ensures every variable matches algorithm requirements. Numerical data may need scaling, categorical fields require encoding, and text must be vectorized. Images and dates must also be formatted correctly. Optimizing data types prevents compatibility issues, preserves information quality, and significantly improves training efficiency and model accuracy.
6. Dataset Splitting and Sampling
Dataset splitting separates data into training, validation, and test sets while preserving distributions. Methods depend on data characteristics, such as temporal ordering for time series. Proper splitting prevents data leakage and ensures fair evaluation. Good sampling strategies create balanced, representative datasets, helping models generalize better during real-world deployment.
Best Practices for Dataset Preparation
Document Decisions: Record all structuring choices, transformations, and rationale. Documentation enables reproducibility and helps debug performance issues later.
Validate Early and Often: Check data quality and structure throughout the process. Early validation catches issues before they compound.
Preserve Raw Data: Maintain original unstructured data alongside processed versions. This enables revisiting decisions and exploring alternative approaches.
Automate Repeatable Steps: Create pipelines automating repetitive structuring tasks. Automation ensures consistency and accelerates iterations.
Common Data Structuring Challenges
Imbalanced Data Distribution
Real-world datasets often have uneven class distribution, requiring sampling, synthetic data, or algorithm tweaks to avoid biased models.
High Dimensionality
Too many features increase complexity and risk of overfitting. Dimensionality reduction and feature selection help focus on the most useful data.
Missing Data Patterns
Missing values may be random or systematic. Proper handling through deletion or imputation prevents biases and improves model reliability.
Multi-Modal Data Integration
Combining text, images, and numerical data requires careful AI integration so models can learn from all relevant information together.
The Amplework Data Preparation Advantage
At Amplework Software, we provide comprehensive Data Preparation Services that transform raw data into training-ready datasets. Our specialists understand that effective AI data modelling requires both technical expertise and domain knowledge.
Our Data Structuring Services Include:
- Complete data assessment and profiling
- Custom schema design for AI workloads
- Advanced feature engineering
- Automated data cleaning pipelines
- Optimized dataset preparation
When you hire data specialists from Amplework, you access professionals experienced in structuring diverse data types across industries. Our team has prepared datasets for computer vision, NLP, time-series forecasting, and recommendation systems.
Also Read : Benefits of ML Consulting Services for AI-Driven Businesses
Final Words
AI data modelling is the foundation of successful machine learning projects. Properly structured data enables models to learn effectively, while poor structuring guarantees mediocre results regardless of algorithm sophistication. Investing time in thorough dataset preparation dramatically improves model performance and project success rates.
Don’t underestimate data structuring. The difference between successful and failed AI projects often lies in data preparation quality rather than algorithm selection. Partner with specialists who understand data structuring for AI deeply.


 sales@amplework.com
sales@amplework.com
 (+91) 9636-962-228
(+91) 9636-962-228